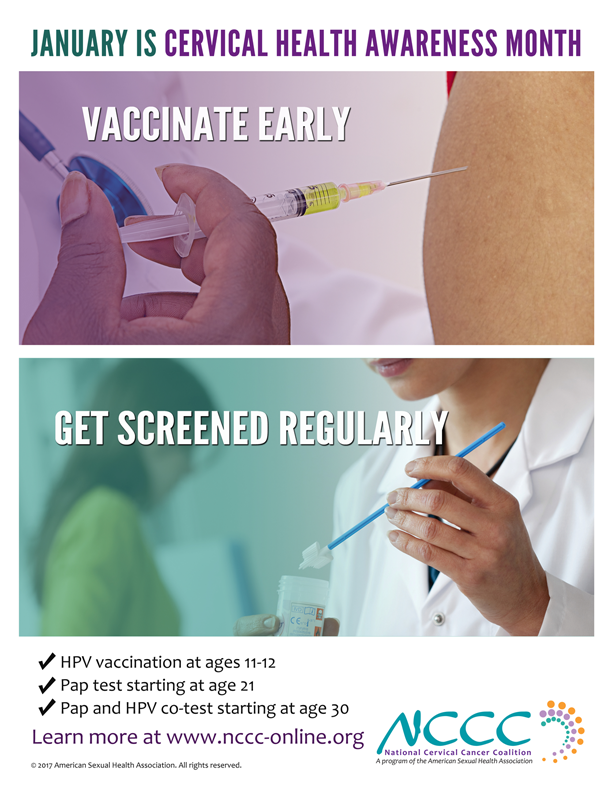
The most important thing you can do to help prevent cervical cancer is to have regular screening tests starting at age 21.
Screening Tests
Two screening tests can help prevent cervical cancer or find it early—
- The Pap test (or Pap smear) looks for precancers, cell changes on the cervix that might become cervical cancer if they are not treated appropriately.
- The HPV test looks for the virus (human papillomavirus) that can cause these cell changes.
Both tests can be done in a doctor’s office or clinic. If you have a low income or do not have health insurance, you may be able to get free or low-cost screening tests through CDC’s National Breast and Cervical Cancer Early Detection Program. Find out if you qualify.
Screening Options
You should get your first Pap test at age 21. If your test result is normal, you can wait three years for your next test.
If you’re 30 years old or older, you have three options—
- You can continue getting a Pap test only. If your test result is normal, you can wait three years for your next test.
- You can get an HPV test only. If your test result is normal, you can wait five years for your next test.
- You can get both an HPV and Pap test together. If your test results are normal, you can wait five years for your next tests.
What Are the Symptoms of Cervical Cancer?
This video discusses the importance of knowing the signs and symptoms of gynecologic cancer.
Early on, cervical cancer may not cause signs and symptoms. Advanced cervical cancer may cause bleeding or discharge from the vagina that is not normal for you, such as bleeding after sex. If you have any of these signs, see your doctor. They may be caused by something other than cancer, but the only way to know is to see your doctor.
Use our Symptoms Diaries to track possible symptoms over a two-week timespan.
Additional Information
Reducing Your Risk of Cervical Cancer (CDC)
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer (CDC)
10 Things to Know About HPV and Cervical Cancer
